The Role of Healthy Nutrition in Learning
Nutrition is a basic need that humans have to survive and be in good health, but it has further implications beyond the scope of mere physical well-being. Proper nutrition may feed the brain in such a way that cognitive functions, focus, and learning are enhanced. Scientific studies have proven that proper nutrition strengthens the brain and enhances such mental processes as memory, decision-making, and problem-solving. It is actually mental productivity and learning that has proved to be of crucial importance in this modern competitive world, both during school years and afterward. It is now time to shift the spotlight to healthy nutrition and the intake of food that enhances the brain for excellence in academics and professional life. The following article will look deeper into the effects healthy nutrition has on the human brain and processes of cognition, showing how healthy balance in a diet raises human capability to learn more.
Role of Nutrition in Brain Development, Learning, and Cognitive Functions
- Nutritional Requirements for Brain Growth
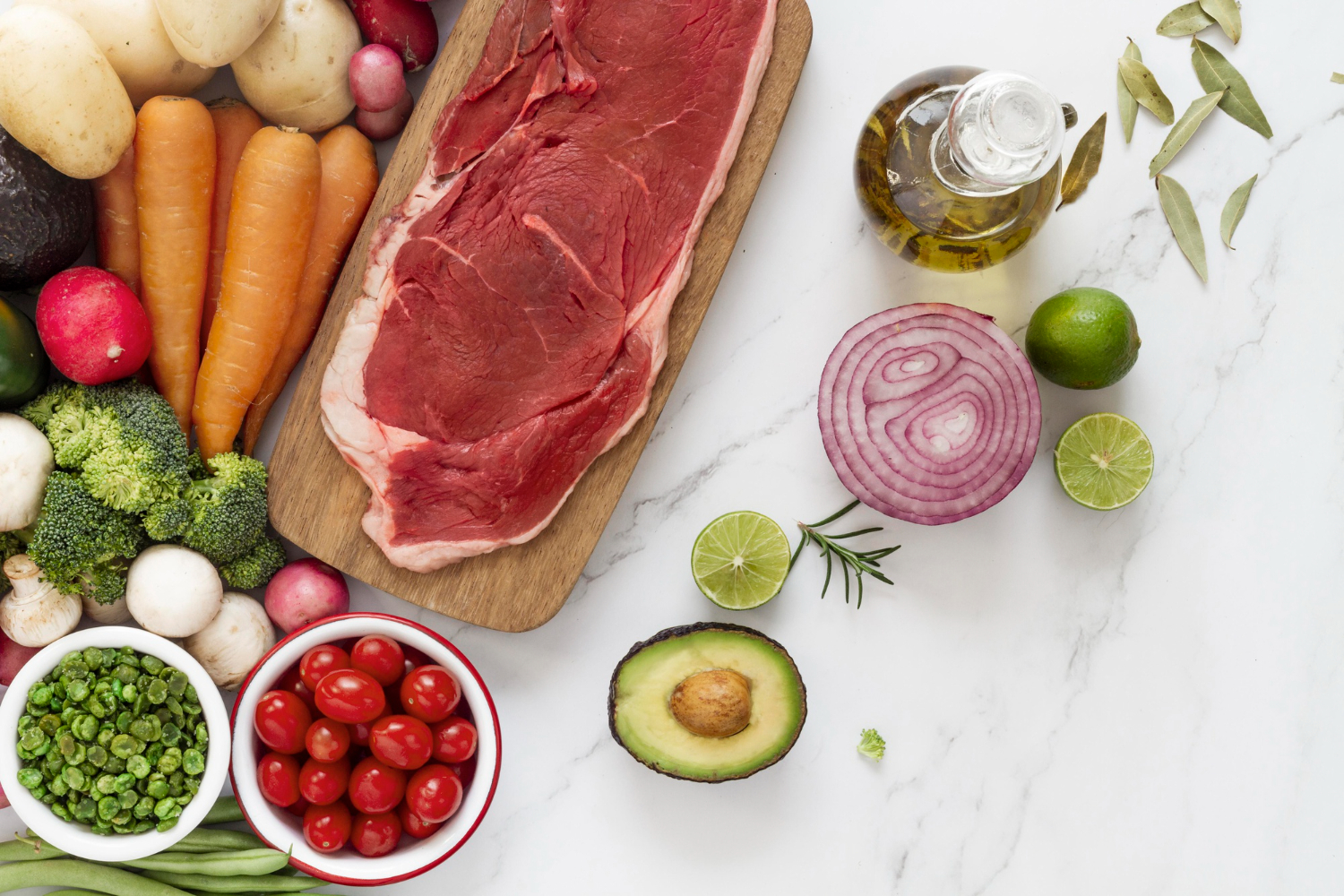
The brain, being at an increasingly developing stage during childhood and adolescence, requires higher nutrition. Elements of proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals are utilized in the construction of neural and structural parts of the brain. Omega-3 fatty acids, iron, and zinc have especially been mentioned in the case of an infant and child for fulfilling the requirement of the developing synapse and for improvement in memory.
- Glucose and Maintenance of Brain Energy Supply
Glucose is believed to be the main source of energy for the brain. Since it is unable to store glucose, the brain is constantly receiving it from the blood. With the low level of glucose, it reduces the concentration and slows down the speed of learning. Ingesting complex carbohydrates such as whole grains allows a person to provide the body with constant amount of glucose and sustain the enhanced work of mental activity.
- Omega-3: Sharpening Concentration, Learning, and Long-term Brain Health
Research has documented that the intake of omega-3s improves focus and diminishes attention deficits, especially among children with learning disabilities like ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder). It also prevents cognitive impairment in old age. Fatty fish, including salmon and tuna, along with flaxseed, chia seeds, canola oil, and walnuts, are rich sources of omega-3s. Another variety of essential fatty acid, omega-6s are involved in many processes throughout the body, including the regulation of the immune system and cell growth. Too much omega-6 without the right balance of omega-3 can lead to inflammation of the body and brain.
- B Vitamins and Neurotransmitter Production
B vitamins, especially B6, B9, and B12, are very important in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine. Neurotransmitters regulate mood and improve memory and concentration. Neurological and cognitive disorders follow the deficiencies of these vitamins, which also cause problems in learning and memory loss.
- Iron’s Role in Mental Performance
Iron is one important constituent in the synthesis of hemoglobin, responsible for the transportation of oxygen throughout the body to the brain. Its deficiency may cause iron deficiency anemia, resulting in mental fatigue, concentration disturbance, and cognitive impairment. Additionally, it reduces the level of dopamine and norepinephrine, further affecting focus, motivation, and learning. Iron deficiency can cause a decrease in concentration and poor academic performance in school children, along with overall poor memory. Iron needs can be met by consuming red meat, spinach, and legumes among other foods.

- Antioxidant-smoothening Brain Protector.
When free radicals act through oxidative stress, it can destroy brain tissue, which reduces cognitive effectiveness. Antioxidants such as vitamin C and E neutralize the free radicals and, thus, protect the brain cells for better memory and focus concentration. This is very important and should be provided through colored fruits and vegetables such as berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens.
- Zinc and Neural Connectivity
Zinc is another mineral important in the development and maturation of the brain, a process termed as neuroplasticity, and normalizing neurotransmitters that improve synaptic performance. It also plays a highly significant role in memory and learning. Inadequate intake of this nutrient may lead to the disturbance in the processes of learning and memory. The best sources of the nutrient are red meat, nuts, and seeds.
- Vitamin D and Cognitive Function
Vitamin D is generally important in overall cognitive functions, either in learning or in memory. It helps regulate the growth and development of neurons and proper synaptic functioning. Synapses are a basis of communication between the nerve cells, and proper functionality directly affects learning and information processing. Vitamin D modulates calcium in the brain, which is very important for the health of neurons and the conduction of nerve impulses. This regulation of calcium enhances the efficiency of synapses, enabling the better transmission of information within the brain, enhancing the ability to learn and remember. Sources include sunlight, fatty fish such as salmon and tuna, egg yolks, and vitamin D-fortified milk and cereals. Vitamin D supplements are also available.
- Magnesium and Mental Relaxation
Magnesium supports neurotransmitter production and regulation, including glutamate and GABA, important in neural messaging, learning, and memory. A deficiency in magnesium disrupts these processes, hence making one’s ability to learn impaired. It helps in reducing stress, hence making one focus and learn better. Nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are good sources of magnesium.
- Choline and Brain Health
Choline is also very important for fetal development; more so during the development of the structural features of the brain and the neurons themselves in utero and in the first few years after birth. The adequate supply of choline during the time a woman is pregnant makes possible an increase in development and activity in the babies’ brains. Moreover, choline prevents the inflammation of the brain cells and thus may save a person from possible neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Choline is rich in egg yolks, red meat, fish, beans, lentils, broccoli, milk, and cheese.
Final Thoughts
Consumption of all vital nutrients on a regular basis would build and boost an individual’s memory, concentration, and ability to learn. Healthy nutrition prevents all sorts of disorder, including problems of learning and concentration, and anxiety, while maintaining emotions and mental health. All the nutrients in balance would support the growth of your brain and optimize the working of your cognition. Healthy eating, though highly essential for the periods of childhood and teenage years, also extends further on into life and forms the bedrock of long and successful cognitive life.
References
Maximize memory function with a nutrient-rich diet