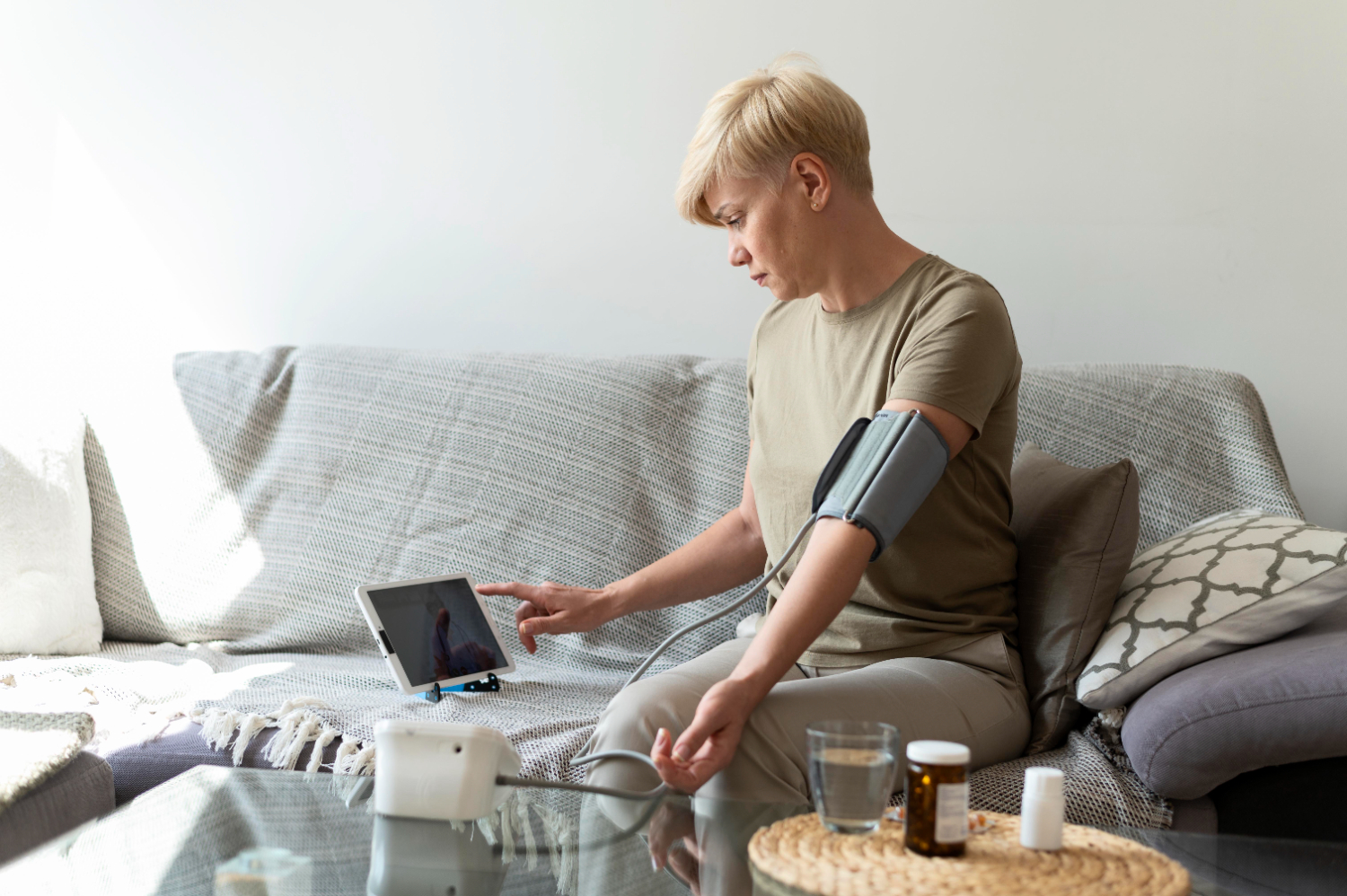
Home Remedies for Low Heart Rate
Bradycardia, or low heart rate, might sound ominous on the first go but it isn’t always indicative of some serious problem. Bradycardia is a condition wherein a person’s heartbeat is less than 60 beats per minute. A lot of people suffer from low heart rate due to various reasons, which may include lifestyle, regular exercise, or even sleep. Though some forms of bradycardia require treatment in the hospital, it is possible to relieve mild and moderate symptoms with the help of certain home remedies, along with the modification in certain aspects of one’s lifestyle. Now in this article, I am going to explain how you can regulate your heartbeat at home and keep it healthy using natural methods, proper nutrition, changes in lifestyle, and exercising.
What is the cause of bradycardia?
There are a number of causes that give rise to bradycardia. Some of the causes are discussed in the section below:
1- Natural/ physiological causes
Some people have a naturally low heartbeat, and this condition depicts the absence of any disease or disorder. For instance, in athletic persons, it is generally seen that their heartbeat is low because of immense physical training that enhances their heart performance. As a result of increased heart-pumping power, the efficiency of the circulatory system increases. In these conditions, bradycardia is a sign of healthiness of heart and has no need for treatment.
2- Heart Disorders
Among the leading causes of bradycardia, one is the problems with the heart system. Damage to the conduction system of the heart, one such problem includes the blocking of the electrical pathways and defects of the heart muscle. Such disorders include coronary artery disease, heart block and sick sinus syndrome.
3- Electrolyte problems
Any disturbance in the electrolytes of the body will inversely affect the functioning of the heart and might lead to bradycardia. Such as a decrease in potassium and magnesium, which is highly responsible for regulating heartbeat.
- Drugs
Some drugs can be one of the causes of bradycardia, mainly drugs that are used for treating heart disease, high blood pressure, or psychiatric problems. Such as beta-blockers, digitalis, digoxin, and tricyclic antidepressants.
- Endocrine disorders
Abnormal functioning of some glands in the body, especially the thyroid gland, may affect the heart rate.
- Infections and inflammatory diseases
Some infection or inflammatory diseases, such as endocarditis and myocarditis, may destroy the heart together with its electrical conducting system.
- Aging
Aging has the potential for deteriorating electrical conduction of the heart. Therefore, in old age a person may encounter with problematic sinus node that, along with other parts, conducts impulses slowly through their electrical system leading to slowed heartbeat, therefore. Its thought to be part of usual aging of heart.
8- Heart attack
A heart attack may also damage the cardiac muscle of the heart and its electrical conducting system. Where the damage is bad, electrical signals will not pass properly through the heart and causes bradycardia.
9- Hypotension
This is when the blood pressure becomes too low, then the body could not provide an adequate amount of blood to the organs, muscles, and even to the heart. This eventually reduces the workload for the heart, that eventually results in a slow heartbeat.

Symptoms of bradycardia
Bradycardia does not present symptoms always. As a matter of fact, for some individuals, the condition will not manifest symptoms at all. But in case the heart rate goes slow enough and blood supply starts to reduce to body organs, a person can note the following symptomatology :
- Irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Extreme tiredness or weakness
- Fainting (syncope) or near-fainting
- Decreased tolerance for physical activity
- Difficulty concentrating or having trouble with memory
Sometimes, bradycardia doesn’t have symptoms and is detectable only during a medical test.
Home remedies for low heart rate
The home remedies for bradycardia are the change in style of life, modification of diet, and application of some natural and relaxing techniques that will contribute to the betterment of the health of the heart and avoiding further aggravation of bradycardia. However, it is crucial that any home remedy should be on the recommendation of a doctor because some forms of bradycardia need to be treated medically with the help of medication. Now I will discuss in detail the home remedies for bradycardia:
1- Dietary change
A healthy and proper diet can reduce the chances of bradycardia or strengthen heart function. The foods which help for a healthy heart are as follows:
- Food containing potassium and magnesium
These two are the major minerals responsible for the electrical balance of the heart; hence, they are considered very important in maintaining the rhythm of the heart. The good sources for these minerals include bananas, potatoes, spinach, avocados, beans, almonds, spinach, nuts, and fatty fish like salmon.
- Omega-3 food
Omega 3 fatty acids are helpful in heart function improvement. It also decreases the conditions of inflammation. Mainly, it contains oily fishes, such as salmon, tuna, and sardines. The supplements are available for it, too.
- A decrease in the intake of salt and saturated fat
Excessive use of salt develops high blood pressure that is the predisposing factor for bradycardia or heart disorders. Reduction of saturated and trans fat can keep heart healthy
- Fiber content based food
The food containing fiber content, fruits, vegetables, whole grains improves heart condition and maintains reduction rate of heart diseases
2- Mild Exercises and Physical Activity
The practice of exercises and routine physical activity reinforces the functioning of the heart along with its pulse. Weighty exercises must be avoided by the patients suffering from bradycardia, and one should focus on gentle exercises. Following are some of the exercises one must follow:
- Walking
It is soft daily exercise that may increase the rate of blood flow and results in strengthening the heart.
- Yoga and meditation
These are the forms of exercises that quiet the nervous system and lower stress, both factors decreasing heart rate;
- Breathing exercises
A good deep breathe or mild aerobics-like swimming is a contributor to strengthening heart function.
3-Managing Stress-Mental Relaxations
The action of the stress is to either increase or decrease the heart rate. Thus, learning to cope with stress and keeping the mind cool may also help in managing bradycardia.
- Meditation
One of the best methods by which the mind can be soothed and the stress can be reduced is meditation. It will help your nervous system and heart rate regulate through daily meditation.
- Deep breathing techniques
Deep, slow breathing minimizes parasympathetic nervous system arousal, allowing the heart rate to return to normal.
- Yoga and tai chi
These exercises help in coupling physical movement with mental focus and deep breathing. Both of them are quite effective in improving heart health and reducing symptoms of bradycardia.
4- Dietary supplements
The supplements that support better functioning of the heart and put their rates in order include : Always Consult a physician prior to the addition of the supplement.
- Magnesium
It is quite useful during regulation of heart rate as it lowers the risk of bradycardia; magnesium helps the muscles function appropriately, which include the heart muscles.
- Coenzyme (Q10)
Antioxidant useful to improve the functioning of hearts and energized cells; studies suggested for a few centuries that the functioning of Co-Q10 for improvements in cardiac health-related to many other heart issues is vital to undertake.
- Omega-3
It promotes or helps maintain your heart condition plus reduces or manages one’s self inflammation by consuming this supplement of such nutrients.
- Potassium
If a deficiency of this essential electrolyte is present then supplements recommended by the doctor may be helpful. This mineral is used by the electrical impulses that control the heartbeat.
5- Heart-friendly drinks
Yes, there are a few heart-friendly drinks, and consuming them will help have control over regular heartbeats and considered good for a heart patient, as :
- Green tea
Green tea has loads of uses that help with your heart’s health, and also with the regulation of your heartbeat. It also possesses immense antioxidant action, which proves of great utility.
- Coconut water
It is an enormous source of potassium and electrolytes. The intake of it assists your body to regulate the quantity between electrolytes and heart rhythm.
- Beetroot juice
Many other studies also reported that beet juice lowers blood pressure as well as maintains heart muscles.
6- Warnings and precautions
- Consult a Doctor
When the heartbeat very slow and regularly dizzy or one often chronically fatigued. He/She must be seen immediately, bradycardia could even require medication treatment and might require even a pacemaker.
- Alcohol and caffeine intake
These are known to affect the heart rate. At times, excess consumption of one or both leads to bradycardia or increased heart rate variability.
- BP and electrolytes
The blood pressure should be monitored along with the occasional testing of the electrolytes as that would prevent the onset of any heart-related disease.

Final Thoughts
The home treatment for slow heartbeat is, in most conditions based on the cause and seriousness of the bradycardia. Generally, a good diet, light physical exercises, and decreasing stress are all advisable to heal one’s heart. The thing is, one should never forget that in some conditions, bradycardia may denote a more serious problem requiring immediate treatment and specialized medical care-which is to say nothing of installing a pacemaker. Anyway, in these situations, it is highly required to consult a doctor and monitor continuously a patient’s condition not to develop dangerous complications.
References