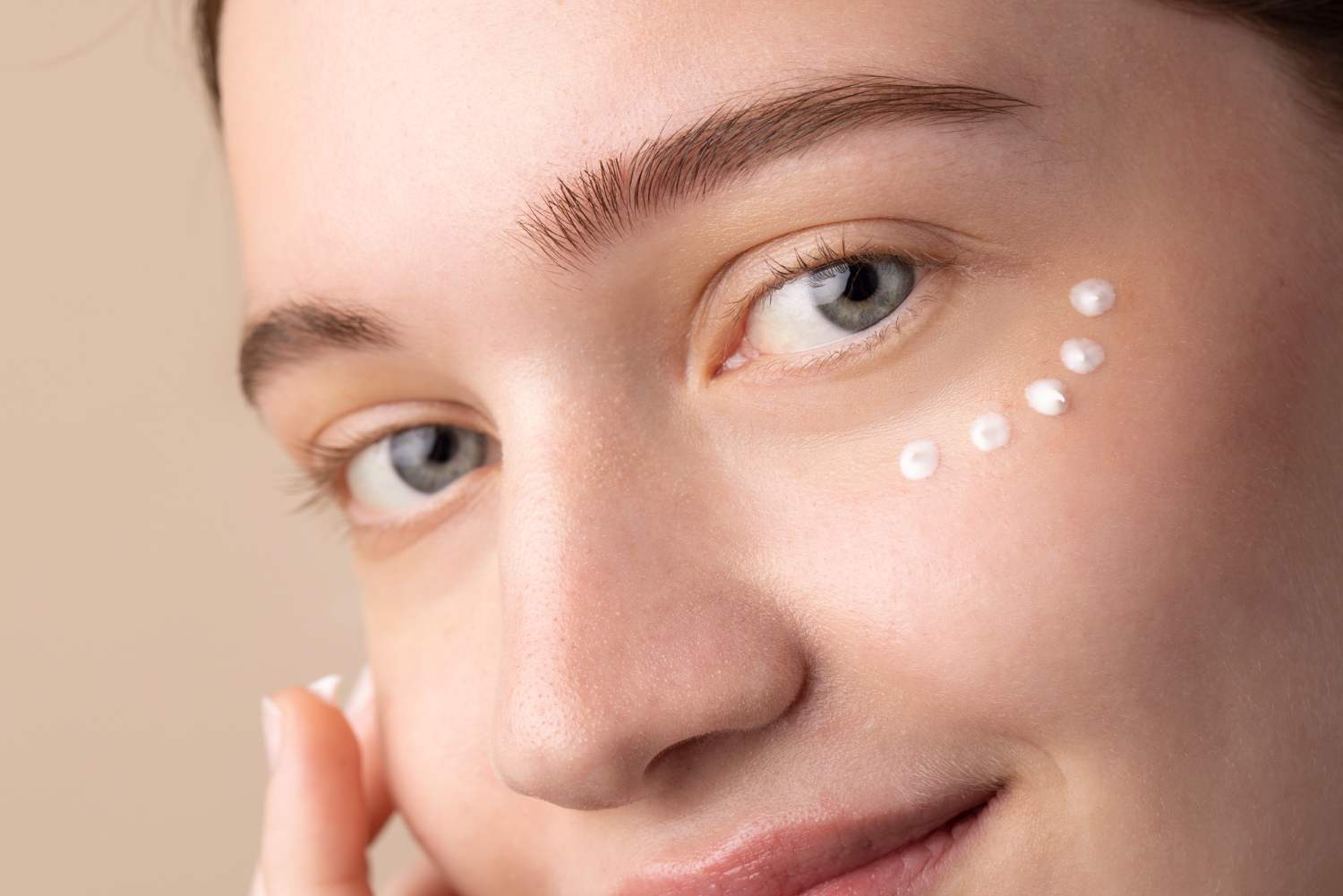
Solace Cooling Eye Cream
When the Eyes Reveal Secrets
Has anyone ever looked into your eyes and, without a single word from you, whispered, ‘You’re weary, aren’t you? This secret doesn’t lie in your tone of voice, nor in the clothes you choose.
It reveals itself in the quietest, most merciless betrayer: the skin around your eyes. Puffiness, darkness, fine lines, fatigue… The very places we cannot hide, nor deny with a smile. But the good news is: just as the eyes are the first to give away your weariness, they can also be the first to bring back your radiance. That’s where the Solace Cooling Eye Cream enters, not as a mere cream,
but as an invisible hand that gently wakes you each morning, and stands guard each night like a loyal companion.
The skin around the eyes, the mirror of truth
The skin around the eyes is structurally quite different from the rest of the face. Its thickness is roughly onethird that of other facial areas, and this delicacy makes even the slightest change quickly visible.
Just one restless night or a few days of high stress and the first signs will appear around your eyes.
- Prolonged stress reveals itself as fine lines.
- Lack of sleep intensifies undereye darkness.
- Poor nutrition or excessive salt and caffeine lead to puffiness.
- Exposure to air pollution or sunlight causes dullness and sagging.
Moreover, this area contains very few oil glands, making it more prone to dryness and moisture loss than other parts of the face. This persistent dryness lays the groundwork for premature wrinkles. That’s why dermatologists always emphasize: caring for the skin around your eyes isn’t a luxury, it’s a daily necessity.

Cooling effect, from the surface of the skin to the depth of the tissue
Solace Cooling Eye Cream offers more than just a refreshing sensation on the skin. Its cooling effect unfolds in layers, each contributing uniquely to the health and appearance of the delicate eye area:
1- Surface Temperature Reduction
- Immediately after application, skin temperature drops.
- This cooling creates a moment of calm, easing inflammation and heat.
- Especially for those exposed to warm or polluted environments, it acts like a quick reset for the skin.
2- Capillary Constriction & Puffiness Reduction
- The coolness causes tiny blood vessels around the eyes to contract.
- This directly reduces swelling from sleepless nights or high salt intake.
- This effect is similar to placing a cold compress on the eyes, but in a targeted and controlled manner.
3- Improved Blood Flow & Oxygenation
- After initial constriction, capillary circulation stabilizes.
- Fresh blood and oxygen reach the cells around the eyes.
- This helps fade dark circles caused by stagnant blood under the skin.
4- Muscle Relaxation & Eye Strain Relief
- Prolonged screen time tightens eye muscles.
- The cream’s coolness acts like a gentle massage, easing tension.
- Result: lighter eyelids and less eye fatigue.
5- Enhanced Skin Barrier Function
- Cooling combined with hydration strengthens the skin’s protective layer.
- Skin retains moisture better and resists external irritants like dust or makeup.
6- Mental & Emotional Impact
- Lower skin temperature sends calming signals to the nervous system.
- Clients often describe a sense of lightness and mental clarity, like sipping cold water on a hot day.
7- LongTerm Daily Benefits
- Continued use makes skin less prone to puffiness and discoloration.
- The muscles around the eyes become more flexible with gentle daily massage.
- This not only creates a more youthful look but also helps prevent premature aging.

A combination of nature and science, the base ingredients of this product
- Retinol gently encourages the skin to produce collagen, like a kind mentor guiding their student toward growth.
- Lavender is that old, calming friend who shows up whenever redness or irritation appears and softly says, “Relax, I’m here.”
- Shea butter is a loyal guardian, preventing moisture from escaping the skin.
- Aloe vera, with its instant cooling effect, feels like a summer breeze on your skin.
- Vitamin E acts as a shield, protecting delicate blood vessels.
- Castor oil quietly supports your lashes and eyelids, asking for nothing in return.
Moments when you need more than Just a Cream
Sometimes this cream is not just a care product; it is a response to specific situations in everyday life:
- When heavy makeup worn for several hours has tired the skin and it needs to breathe.
- When seasonal allergies or a sudden insect bite has inflamed the skin around your eyes.
- When you’ve been up all-night studying and you’re searching for freshness in the mirror come morning.
- When you rise from your desk with a tension headache and crave instant calm.
- Or even when you notice fine lines on your forehead left behind by long hours of frowning.
In all these moments, Solace Cooling Eye Cream becomes more than a product. It’s a brief return to yourself; a touch of care, a breath of cool, a quiet reset.
How to use this little companion?
The secret to this cream’s effectiveness lies in using it the right way.
- Cleanse the skin around your eyes.
- Take a small amount with your ring finger; the gentlest one.
- Tap lightly until absorbed.
- Repeat morning and night.
Over time, you’ll notice how these few seconds a day transform not just your skin, but your confidence.
Why Solace?
Solace is more than just a brand. Behind the name lies a simple yet profound philosophy: skincare should be scientific, safe, and deeply attuned to real human needs. We believe skin isn’t just a physical layer, it’s part of our identity and emotional state. That’s why products like Solace Cooling Eye Cream are designed with more than just surface-level concerns in mind. This cream is meant to give your skin a chance to heal, refresh your gaze, and offer a sense of calm that doesn’t get lost in the chaos of daily life.
Final Thoughts
Eyes are the first thing people notice and the first to reveal signs of fatigue and the passage of time. Left unattended, these signs grow more visible each day. But with care, your eyes can reflect years of youthfulness, vibrance, and confidence. Solace Cooling Eye Cream helps you choose what your eyes reveal at first glance: exhaustion or vitality?