Thyroid and the Not-so-obvious Function of Fruits in Your Health
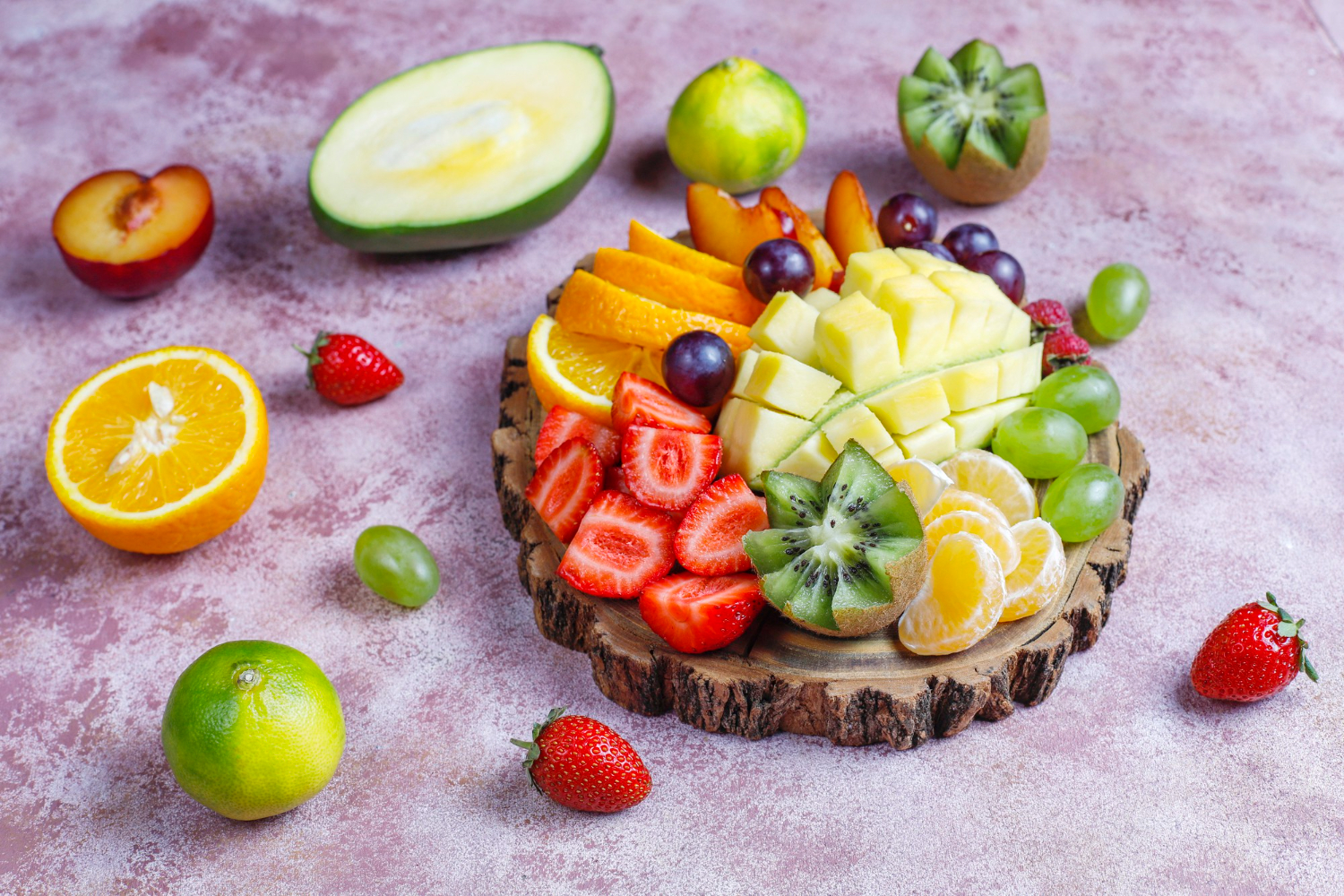
Are you getting tired easily, why so fat and no cause behind it, or is your skin drying and becoming dull? Hypothyroidism is a very common metabolic disorder which affects a lot of people, but fortunately, that food can slow it down. You will be surprised to learn that the foods you eat on your plate directly affect your thyroid function. Fruits are among the many, some of the most important foods that supply you with the nutritional requirement. Fruits are those foods that enhance some thyroid function by supplying proper nutrients while some affect the absorption of iodine and aggravate the condition. In this article, I will discuss some helpful fruits that are advantageous for thyroid enhancement, then discuss harmful fruits for hypothyroid patients. So if you are interested in a natural way of boosting your thyroid function, don’t hesitate to read this article!
Fruit that is helpful for hypothyroidism
1- Apples: Natural Detoxification to Support the Thyroid
Apples are one of the healthier fruits to consume for overall body health, but how necessary it is for the thyroid isn’t really understood. Apples do contain pectin, a soluble fiber that draws the heavy metals from the body, including mercury and lead. These are the heavy metals that will destroy thyroid function, so consuming apples will clear the body and assist in promoting thyroid function. The best way to consume apples is:
- Consume a raw apple along with its skin to receive the maximum amount of fiber and antioxidants.
- Apple slices consumed with cinnamon have a metabolic stimulating effect and influence the thyroid gland more profoundly.
2- Bananas: Iodine-Rich Source and Thyroid Stimulator
The most important component utilized in the synthesis of thyroid hormones is iodine, and its lack leads to hypothyroidism. Bananas contain a high amount of iodine, and their use aids in the improvement of the functioning of this gland. Bananas also contain vitamin B6 and magnesium that calm inflammation of the thyroid gland and regularize the secretion of hormones. The proper method of banana use is as follows:
- Snack on bananas, or with Greek yogurt for added value.
- Smoothie of pureed bananas with walnuts (selenium-rich) could be profoundly therapeutic to the thyroid.
3- Pomegranate: nature’s pill to get the metabolic engine and energy flowing
Fatigue and weakness are some of the signs of hypothyroidism. Pomegranate contains high antioxidant properties and iron, which help in oxygenation of the cells and give energy. Besides this, it also increases metabolism and reduces inflammation in the body.
- A glass of freshly squeezed pomegranate juice in the morning can give energy for the whole day.
- Add pomegranate seeds to salads or yogurt to benefit from their properties.
4- Oranges and lemons: strengthening of the immune system and inflammation reduction of the thyroid
Hypothyroidism can debilitate the immune system, but oranges, lemons, and grapefruits contain plenty of vitamin C, which boosts the immune system and inflammation reduces. These fruits also facilitate iron absorption, which is required for thyroid activity. Following is the best way to utilize citrus fruits:
- Drink one glass of fresh orange juice every day.
- Consume a few drops of lemon juice diluted in lukewarm water on an empty stomach to detox the body and activate thyroid function.
5- Figs: hormonal regulator and rich in iron
Hypothyroid patients are also usually deficient in iron, and this decreases the level of thyroid hormones. Figs are rich in fiber, magnesium, and iron, all of which are good for the thyroid and hormonal system. The following is how to take figs:
- Soak figs in water overnight and consume water along with the figs in the morning.
- Consume raw nuts like almonds and walnuts and selenium-rich figs that are healthy fat for thyroid.

Fruits that are unsuitable for Hypothyroidism
1- Nectarine and peach: interference with iodine consumption and adverse impact on thyroid function
Nectarine and peach are among the goiterogenic content-rich fruits. They will lower the absorption of iodine as well as suppress the secretion of thyroid hormones. Since iodine is one of the most significant elements linked with thyroid function, excess intake of this element due to these fruits will enhance hypothyroidism. The proper consumption of peach and nectarine is described below:
- If you have no iodine, then you will need to cut down on the intake of these fruits.
- Eat them if you must, but in small quantities and combined with other iodine-containing food sources such as fish and milk.
2- Strawberries: Why can’t hypothyroid patients with certain conditions eat it?
Strawberries also happen to be one of the fruits rich in goitrogenic content. Though the fruit is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, they are a issue to be taken in enormous amounts when you are deficient in iodine. Being hypothyroid as well as deficient in iodine simultaneously is a bad idea, and when you take a lot of strawberries, it is even worse. The best way to take strawberries is:
- It should be consumed in small quantities and along with iodine foods such as seaweed or yogurt.
- On the occurrence of any allergy or aggravation of hypothyroidism, its use should be discontinued.
3- Pears and carrots: impact of their own components on thyroid hormones
Though pears are extremely healthy and rich in vitamins, they contain trace elements of certain compounds in them that don’t quite agree with the thyroid. To be more specific, if its consumption is in large quantities, then it will slow down the thyroid in the long run. The ideal manner in which the pear must be consumed is as follows:
- It must be consumed in small quantities.
- Its combination with selenium-rich foods like nuts can reduce the side effects.

Points to Ponder in Choosing Fruit for Hypothyroidism Patients
With ideas on what fruits are beneficial and harmful to the thyroid, it is advisable that take some of the points into consideration on which you have to think carefully while making a good choice.
1- Why fruit balance is required
There is no fruit that will trigger or aggravate hypothyroidism. The key is a balanced diet. Even goitrogenic fruit in moderation is safe.
2- Best Forms of Fruit Consumption for Optimum Absorption
In certain cases, the consumption form of fruit can change the effect of such fruit on thyroid function. Some of the best forms of consumption of healthy fruit without triggering the toxic effects of such fruit are:
- Fruits should be mixed with other foods such as Greek yogurt, nuts, and seeds to maximize nutrient uptake.
- Citrus fruits, for instance, should be consumed in the morning for optimal uptake of nutrients.
Final Thoughts
There is no food that can cure or aggravate the disease but healthy diet and wise choice is the best defense in fighting body health. Understanding food ingredients and their implications for the function of the thyroid gland can manage proper diet and reduce drug therapy. Last but not least, healthy life, along with healthy diet, physical activity, and stress reduction, improves the function of the thyroid gland and quality of life. If you are experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism, speak to your doctor and dietician about this, which can provide more individualized information to alter your diet based on this.
References